

Note: it is only depreciated, not yet removed. In Java 11, the support for Java browser plugins is removed and due to which the Applet API has been deprecated.These are the following deprecations which are done in between Java 8 and Java 11. Let's understand the difference between both versions of Java on the basis of deprecations. A new schema introduces for the versions. It is another change between Java 8 and Java 11 which defines how the version strings should be formatted. The type of infection prevents repeating the same text over and over again by affecting only local variables. The var keyword is a developer-friendly keyword that helps us to reduce the boilerplate coding.
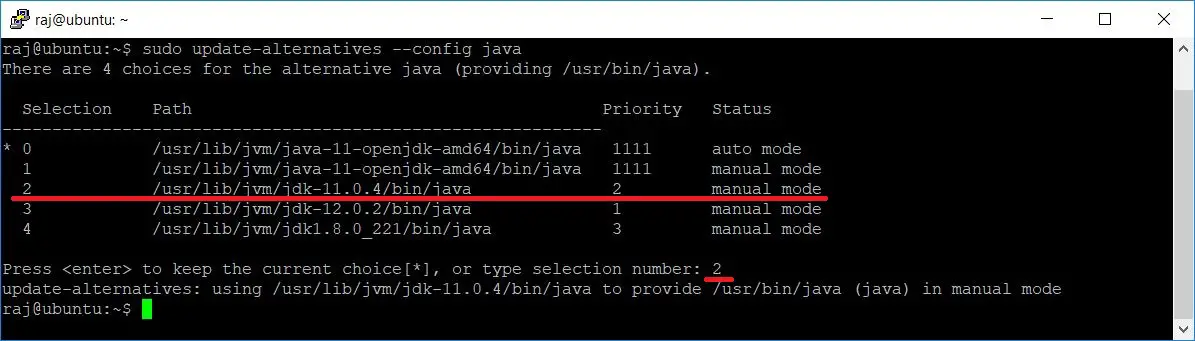
In Java 10, the var keyword was introduced, which improved in Java 11. Multi-jar provides a way to still the code with the latest features of Java 11 while maintaining support and functionality for Java 8 clients. It is one of the features which is added in Java 11. The -release 8 is an example that we need to compile at a Java 8 level. It is a very simple combination of -target and -source that allows us -bootclasspath for compiling at the older version. It behaves in the same way as the Java 8 compile code. We can compile our code without compiling the file by simply placed it into the module having no name. Modularity allows us to test our application easily and also managing access to what parts of our code are public-facing. By using modularity, we can split our programs or applications into different modules. It is one of the biggest changes that have been added in Java 9. The Modularity feature is not available in Java 8. Below are the features which are added in the four and a half years in between these two versions. Java 11 comes with new features to provide more functionality.

Java 11 was released after four years of releasing Java 8.

It is an open-source reference implementation of Java SE platform version 11. Java 11 was publicly available on 25 September 2018 in the market.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
